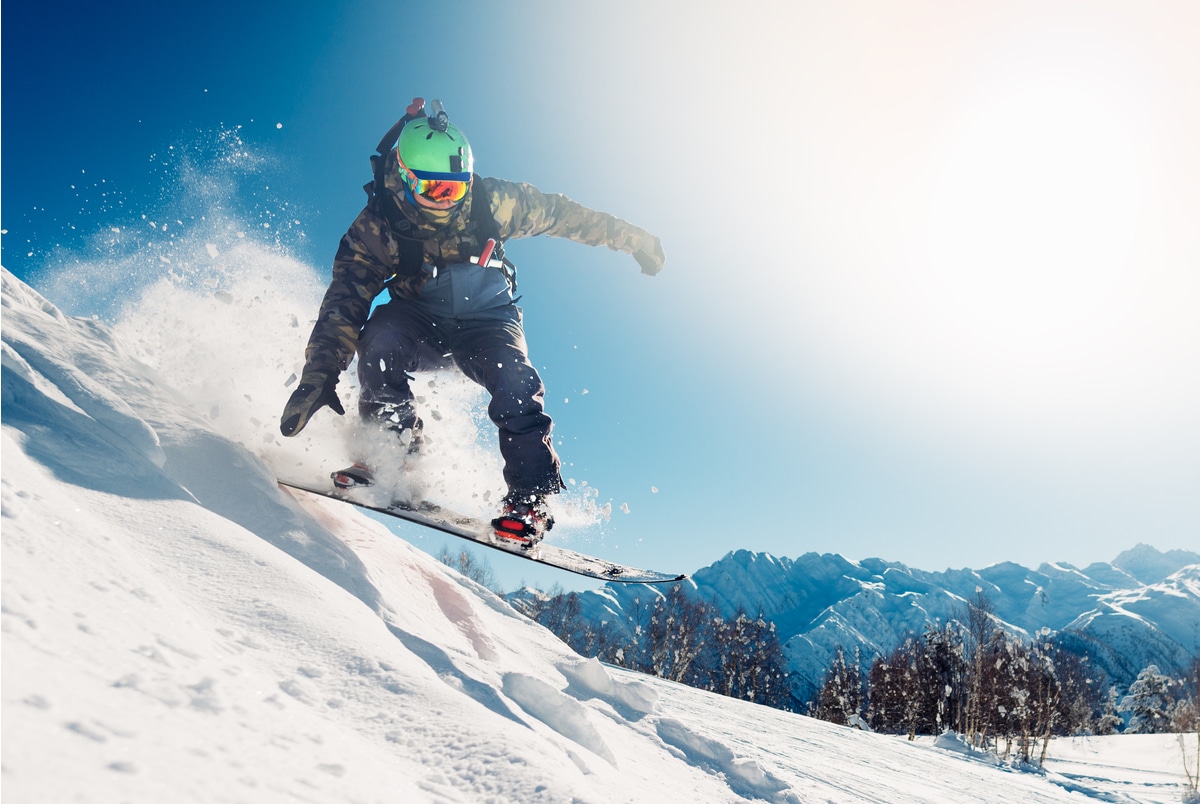
Wrist injuries come top of the list of the most common snowboarding injuries. Over the next few months, as the winter sports season gets into full swing, many snowboarders, and to lesser extent skiers, will return from the slopes with significant wrist injuries.
Due to the fact that Snowboarders have both their feet strapped to the board, the only way to break their fall is by putting out their hands.
There are a couple of things that can significantly reduce the risk of injury.
- Take lessons to learn how to fall and to up your skill level. Try and fall either by rolling backwards onto your buttocks and back, or forwards onto your knees and forearms.
- There are also wrist guards available which reduce the chance of serious injury. Longer guards that extend some way up the forearm should ideally be used.
What Injuries of the Wrist can Occur?
When falls occur at speed during skiing or snowboarding, three main structures in the wrist are most at risk:
- the distal Radius
- the Scaphoid
- the Scapholunate Ligament
Typically, a broken bone is accompanied by a cracking noise. Regardless of severity, there will likely be some swelling, bruising, and pain.
Perhaps unsurprisingly, fractures of the forearm bones, usually the radius, are the most common in younger patients with strong bones. The force required to cause such a fracture is higher – meaning that fractures often have more complex patterns than the routine “Colles fracture” sustained by older patients in lower-energy falls. X-rays will demonstrate the fracture, but CT scanning is helpful in planning surgery for comminuted intra-articular fractures.
Fractures of the carpal bones, especially the scaphoid are sometimes difficult to diagnose, and do not always heal well. The diagnosis of a fractured scaphoid is suspected if there is tenderness in the “anatomical snuff box” of the wrist, but scaphoid X-rays soon after the injury can be normal. MRI scanning is the most sensitive way of detecting a fracture that does not appear on X-ray (known as occult fracture). Risk factors for non-union include the presence of displacement of more than 2mm, fractures that are located within the proximal third of the scaphoid, and a delayed diagnosis. Scaphoid fractures are also less likely to heal in smokers.
Finally, the least common but probably most difficult injury to treat is that of a rupture of the Scapholunate Ligament. This ligament can also be torn in combination with a distal radius fracture. A high index of suspicion is required to pick up this injury, and anyone with significant swelling and/or tenderness over the scapholunate ligament should be assessed by a wrist specialist. MRI scanning can be very helpful in making the diagnosis, although arthroscopic examination of the ligament is said to represent the gold standard.
Many other structures in the wrist and hand can be injured by falls at high speed, including the ligaments that hold the radius and ulna together, the triangular fibrocartilage, other carpal bones, and the ulnar collateral ligament of the thumb MCP joint (known as “skier’s thumb”). However the injuries mentioned above are the most common in snowboarders.
Management of Wrist Injuries
Distal Radius Fractures
Fractures of the distal radius that are undisplaced or minimally displaced can be well treated with cast immobilisation for a period of six weeks. A course of physiotherapy will be required once the cast is removed to regain both range of motion and strength.
Displaced fractures are usually manipulated under anaesthetic or sedation into a better position, when the patient is first seen in an emergency department. Definitive surgical treatment can then be planned, and will be required if the manipulation is only partially successful, if the joint surface is severely affected, or if the fracture re-displaces in the initial cast.
There are many ways to surgically reduce and stabilise a distal radial fracture, but in the majority of cases I use a specialised form of plate and screws known as a “volar locking plate”. The advantages of this form of fixation are:
- Provision of stability to the fracture site while it heals
- Early rehabilitation – the patient can start exercises within the first week of surgery, under the guidance of a hand therapist
- No need for further surgery – the plate can almost always be left in situ
- Earlier recovery of strength and range of motion than with more traditional techniques such as “K-wiring”
- Can be used for treatment of complex intra-articular fractures
Scaphoid Fractures
Fractures of the distal scaphoid and undisplaced fractures of the waist of the scaphoid usually do well in a cast but may need 8 or even 12 weeks of immobilisation to heal. Fractures of the proximal pole of the scaphoid and displaced fractures of the waist do not heal so well.
In the acute situation, I will offer patients with these injuries a minimally invasive operation – a “percutaneous fixation” or “mini-open fixation” – depending on the exact position of the fracture. A special type of screw is used which is buried within the bone and effectively compresses the fracture site, encouraging good fracture union. This again has the advantage of minimising the time it is necessary to wear a cast, as well as increasing the likelihood of healing. Patients with undisplaced fractures can also elect to have this procedure carried out if they wish to avoid 8 to 12 weeks of cast immobilisation.
Scapholunate Ligament Injuries
Acute complete ruptures of this ligament require operative repair, and wires are inserted across the relevant bones to protect the repair for ten weeks. Partial injuries may require wiring for a period of six weeks. The wires are then removed before physiotherapy is commenced. Some residual stiffness of the wrist is common in the long term, and failure of the ligament repair can occur, in which case, operative reconstruction of the ligament may be considered.
Key Points
- Snowboarders should learn how to fall safely, and should wear longer length wrist guards to avoid serious wrist injury
- The distal end of the radius, the scaphoid bone and the scapholunate ligament are most at risk from a fall whilst snowboarding
- Specialised “locking plates” placed on the palmar aspect of the radius are used to allow early rehabilitation of the wrist after distal radius fracture
- Scaphoid fractures can be treated with minimally invasive surgical fixation to increase the chance of healing and avoid prolonged cast immobilisation.
By Consultant Hand and Wrist Surgeon Sam Gidwani
January 2022